|
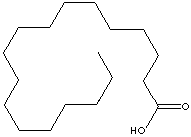
STEARIC ACID
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CAS NO. |
57-11-4 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 200-313-4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | CH3(CH2)16COOH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 284.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
2915.70.0120 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES |
C(CCCCCCCCCCC)CCCCCC(=O)O |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | n-Octadecanoate; 1-Heptadecanecarboxylic acid; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| n-Octadecylic acid; Cetylacetic acid; Acide octadecylique; Acide stearique; Stearophanic acid; Octadecanoic acid; Other CAS RN: 8013-28-3, 8023-06-1, 8037-83-0, 8037-40-9, 8039-54-1, 8039-53-0, 8039-52-9, 8039-51-8, 39390-61-9, 58392-66-8, 82497-27-6, 134503-33-6, 197923-10-7, 294203-07-9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
EXTRA NOTES |
EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 079082, FEMA No. 3035 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Fatty Acid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | White to yellowish solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 67 - 69 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 361 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 0.1-1 g/100 ml at 23 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OH RATE | 2.25E-11 (cm3/molecule-sec at 25 C Atmospheric ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
9.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HENRY LAW CONSTANT | 4.76E-07 (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) Constant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
196 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
EXTERNAL LINKS &GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Fatty Acids are aliphatic carboxylic acid with varying hydrocarbon lengths at one end of the chain joined to terminal carboxyl (-COOH) group at the other end. The general formula is R-(CH2)n-COOH. Fatty acids are predominantly unbranched and those with even numbers of carbon atoms between 12 and 22 carbons long react with glycerol to form lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells) in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Fatty acids all have common names respectively lauric (C12), myrIstic (C14), palmitic (C16), stearic (C18), oleic (C18, unsaturated), and linoleic (C18, polyunsaturated) acids. The saturated fatty acids have no double bonds, while oleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid has one double bond (also described as olefinic) and polyunsaturated fatty acids like linolenic acid contain two or more double bonds. Lauric acid (also called Dodecanoic acid) is the main acid in coconut oil (45 - 50 percent) and palm kernel oil (45 - 55 percent). Nutmeg butter is rich in myristic acid (also called Tetradecanoic acid ) which constitutes 60-75 percent of the fatty-acid content. Palmitic acid(also called Hexadecylic acid ) constitutes between 20 and 30 percent of most animal fats and is also an important constituent of most vegetable fats (35 - 45 percent of palm oil). Stearic acid (also called Octadecanoic Acid) is nature's most common long-chain fatty acids, derived from animal and vegetable fats. It is widely used as a lubricant and as an additive in industrial preparations. It is used in the manufacture of metallic stearates, pharmaceuticals, soaps, cosmetics, and food packaging. It is also used as a softener, accelerator activator and dispersing agent in rubbers. Oleic acid (systematic chemical name is cis-octadec-9-enoic acid) is the most abundant of the unsaturated fatty acids in nature. Stearic Acid is widely used as a lubricant and as an additive in industrial preparations. It is used in the manufacture of metallic stearates, pharmaceuticals, soaps, cosmetics, and food packaging. It is also used as a softener, accelerator activator and dispersing agent in rubbers. INDIVIDUAL SATURATED FATTY ACIDS
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PALM OIL ACID (HARDENED) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
Bead |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IODINE VALUE |
0.5 max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACID VALUE | 208 - 210 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SAP VALUE | 209 - 211 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TITER | 54 - 56 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COLOR | 0.5 R / 2.5 Y | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CARBON DISTRIBUTION |
C14 (1% max) + C16 (62% max) + C18 (45% max) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 25kgs
in bag , 17mts in Container | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FAT |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Commercial fats
produced by organic processes in plants are palm, coconut, palm kernel,
sunflower, soybean, and other oils. Their main components are triolein and
triglyceryl esters of stearic (C18), palmitic (C16), myristic(C14), lauric
(C12), oleic (C18:1), and other fatty acids. Tallow is a refined hard fat
extracted from fatty deposits of animals, especially from suet (fatty tissues
around the kidneys of cattle and sheep). The molecules of most natural fatty
acids have an even number of carbon chains due to the linkage together by ester
units. Analogous compounds of odd numbers carbon chain fatty acids can be made
synthetically. All fats are insoluble in water and have lighter weight than
water. Industrial fats can be sub-classified as fat, grease or oil depending on
melting point. Fats that are liquid at room temperature are referred to oil.
Grease has a higher initial viscosity than oil. It is used as a lubricant. The
organic processes to convert fats to fatty acids (or esters) and glycerol is
called oleochemistry. Fatty acids and glycerol are produced by hydrolysis
(addition reaction of water molecule with cleavage of parent molecules) of the
triglycerides. Fatty esters are produced by esterification reaction. Coconut or
palm oils are better source to get saturated fatty acids than sunflower, soybean
or rapeseed oils which have more unsaturated fatty acids composition of
triglycerides. Tall oil fatty acid (TOFA) is a low cost unsaturated fatty
acid (oleic acid) and is a source of low boiling point fatty acids.
It is an alternative to tallow fatty acid in soap applications. Generally,
commercial coconut fatty acid has carbon chain composition of; C10 (5% max) +
C12 (45 - 55%) + C14 (20 - 25%) + C16 (10 - 15 %) + C18 (10 - 15% max, including
unsaturated fatty acids). Fats are used to make soap, food products, cosmetics,
and candles, and lubricants. They are wisely used in producing synthetic
surfactants.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||